Sources of Air Pollution (An overview)
There are many natural sources of air pollution such as eruption of volcanoes, biological decay and lightning-caused forest fire. Naturally, the Earth already has its own air pollution loading. However, industrialization or just everyday routines has become added burden to the existing air pollution loading. Sources of air pollution are as explained below.
Industrial and development activities
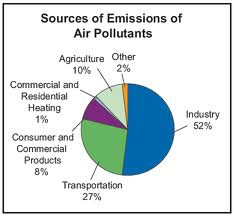
Malaysia’s economic growth is mainly based on its manufacturing (especially electronics), chemical and rubber industries. But higher production rates also lead to higher emissions of organic and inorganic gases, chemicals and dust.
Besides emissions of toxic dust, unplanned and uncontrolled development of industrial premises or zones leads to noise pollution and vibration disturbance. The use of conventional piling methods and the sound of exhaust fans in factories are some of the common activities that generate high sound level.
Modern society is highly dependent on motorized transportation such as cars, trucks, and railways. Movement of people and goods requires energy which relies mostly on the burning of fossil fuels, thus causing emissions and noise with adverse local effects.
The air quality of the different transport modes depends on the kind of energy, engine technology and the amount of energy consumed. Within the transport sector motorized road traffic is the main emission source while public transport is environmentally friendlier than passenger cars.
The air quality of the different transport modes depends on the kind of energy, engine technology and the amount of energy consumed. Within the transport sector motorized road traffic is the main emission source while public transport is environmentally friendlier than passenger cars.
In 2004, nearly 14 million vehicles were registered in Malaysia, almost double the number from a decade ago.The number will increase in the next few years, with higher disposable incomes, rural-urban migration and the lack of efficient public transport systems.
Most of the energy is produced in conventional power plants burning fossil fuels like natural gas, oil or coal. The effectiveness of these power plants is about 35 to 40 per cent with the remaining chemical energy converted into heat.
At the moment, Malaysia produces 86% of its electricity in conventional power plants and 14% in hydroelectric power plants.
At the moment, Malaysia produces 86% of its electricity in conventional power plants and 14% in hydroelectric power plants.
Everyday Routine
Household contribute to air pollution mainly through the use of energy that is required to run machines and electrical appliances such as refrigerators. Refrigerators and air conditioners not only consume energy but they pollute the environment when their coolant fluids release Chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) into the atmosphere. Chemicals used in houses and gardens are also sources of pollution as well as toxic waste.
Burning of older existing plantations for re-planting creates large amounts of soot particles. These soot particles can be blown over long distances and are mainly responsible for the haze that often covers the sky above Malaysia. These fires not only pollute the air but also destroy the rich habitat of the flora and fauna.


No comments:
Post a Comment